The most detailed PCB material related knowledge
1. PCB board purchase principle
1) For general electronic products, FR4 epoxy glass fiber substrate is used
2) For high ambient temperature or flexible circuit board, polyimide glass fiber substrate is used
3) For high frequency circuit, PTFE glass fiber substrate is needed
4) For electronic products with high heat dissipation requirements, metal substrate should be used.
2. Factors to be considered when selecting PCB materials
(1) The substrate with high glass transition temperature (TG) should be selected properly, and TG should be higher than the circuit working temperature.
(2) Low CTE is required. Because the thermal expansion coefficient of X, Y and thickness direction is not consistent, it is easy to cause PCB deformation, even lead to metallization hole fracture and damage components.
(3) High heat resistance is required. It is generally required that PCB can have heat resistance of 250 ℃ / 50s.
(4) Good flatness is required. PCB warpage requirement of SMT is less than 0. 0075mm/mm.
(5) In terms of electrical performance, high-frequency circuit requires the selection of materials with high dielectric constant and low dielectric loss. Insulation resistance, voltage withstand strength and arc resistance should meet the product requirements.
3. About metal heat dissipation substrate
At present, there are aluminum substrate and copper substrate. As a professional manufacturer of metal substrate, Rocket PCB is recommended to use aluminum substrate with high cost performance. Although copper substrate is better than aluminum in thermal conductivity, its cost and weight are much higher than that of aluminum, so it is better to use aluminum substrate. On the other hand, at present, many manufacturers of high-power lamps adopt temperature control method, that is to add a temperature control switch at the place where the aluminum substrate may generate the highest temperature, and set its temperature value (for example, about 65 ℃), when the temperature here is higher than this value, the current will be reduced immediately. Although the light is a little dim, but the general people may not pay attention to these, so this method is still feasible.
4. The common CCL brands
The common CCL brands in China are: Shengyi, Kingboard, Haigang, Hongren, Guoji, Hezheng, South Asia, Panasonic, Hitachi, Zhaoyuan, Jinbao, Tongling, Huarui, Doushan, Jigao, getek, Isola, neclo, Rogers (Rogers), Taconic, arllon polyclad, NETEC.
5. Substrate
The base material is generally classified according to the insulation part of the substrate. The common raw materials are electrical wood, fiberglass board, and various types of plastic board. PCB manufacturers generally use an insulating part made of glass fiber, non-woven material and resin, and then press epoxy resin and copper foil into "prepreg".
The common base materials and main components are as follows:
FR-1 -- phenolic cotton paper, the base material is commonly known as electric board (higher economic efficiency than FR-2
FR-2 -- phenolic cotton paper
Fr-3 - cotton paper, epoxy resin
FR-4 - woven glass, epoxy resin
FR-5 -- glass cloth, epoxy resin
FR-6 -- ground glass, polyester
G-10 - glass cloth, epoxy resin
CEM-1 -- cotton paper, epoxy resin (flame retardant)
Cem-2 -- cotton paper, epoxy resin (non flame retardant)
CEM-3 -- glass cloth, epoxy resin
Cem-4 -- glass cloth, epoxy resin
Cem-5 -- glass cloth, polyesters
Ain -- aluminum nitride
SiC -- silicon carbide
Copper foil
Prepreg
Core board
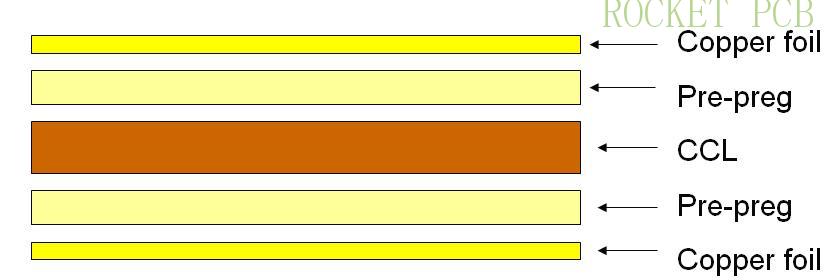

Copper foil

Prepreg
1. According to different reinforcement materials (the most commonly used classification method)
Paper substrate (FR-1, FR-2, fr-3)
Epoxy glass fiber cloth substrate (FR-4, FR-5)
Composite substrate (CEM-1, CEM-3)
HDI substrate (RCC)
Special base materials (metal base material, ceramic base material, thermoplastic base material, etc. )
2. According to different resins
Phenolic resin board
Epoxy resin board
Polyester resin board
BT resin board
PI resin board
3. According to the flame retardant performance
Flame retardant (UL94-V0, UL94-V1)
Non flame retardant (UL94-HB)
Non flame retardant | Flame retardant (V-0, V-1) | ||
Rigid board | Paper substrate | XPC、XXXPC | FR-1、FR-2、FR-3 |
Composite substrate | CEM-2、CEM-4 | CEM-1、CEM-3 CEM-5 | |
Glass fiber cloth substrate | G-10、G-11 | FR-4、FR-5 | |
PI board, PTFE board, BT board, PPE (PPO) board, CE board, etc. | |||
Resin coated copper foil (RCC), metal substrate, ceramic substrate, etc. | |||
Flexible board | Polyester film flexible copper clad laminate, polyimide film flexible copper clad laminate | ||
(1) The epoxy glass fiber cloth copper clad laminate has high strength, good heat resistance and good dielectric property. The through-hole of the base plate can be metallized to realize the circuit conduction between two-sided and multi-layer printing layers. The epoxy glass fiber cloth copper-clad laminate is the most widely used and most widely used type among all the qualities of the copper clad laminate. It is widely used in mobile communication, digital TV, satellite, radar and other products. Among all kinds of CCL in the world, paper-based CCL and epoxy gfrp-ccl account for about 92%
(2) In NEMA standard, there are four types of epoxy glass fiber cloth copper clad laminates: G10 (non group combustion), G11 (retained thermal strength, not flame retardant), FR-4 (flame retardant), FR-5 (retained thermal strength, flame retardant). At present, FR-4 board accounts for more than 90% of the total amount of epoxy glass fiber cloth copper clad laminate, which has developed into a general term suitable for different applications;
The main components of epoxy glass fiber cloth substrate are as follows:
Type of E glass fiber paper
7628 2116, 1080, 3313, 1500, 106, etc

Epoxy resin (resin)
Bifunctional resin, multi-functional group resin;
Copper foil
Electrolytic copper foil (1 / 3oz, 1 / 2oz, 1oz, 2oz, 3oz, 5oz)
Calendered copper foil (mainly used in flexible copper clad laminate)
Curing agent
DICY
NOVOLAC
Glass cloth
Common specifications of prepreg
model | 1080 | 2116L | 2116A | 2116H | 1500 | 7628L | 7628A | 7628H | 7628M |
Thickness mil | 3 | 4 | 4. 5 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 7. 5 | 9. 3 | 8 |
Resin
In the production process of substrate materials, polymer resin is one of the important raw materials. According to the requirements of different types of substrates, different resins can be used, including phenolic resin, epoxy resin, melamine formaldehyde resin, polyester resin and some special resins such as pi, PTFE, BT and PPE.
Copper foil
According to the different preparation methods of copper foil, it can be divided into calendered copper foil and electrolytic copper foil.
(1) Calendered copper foil is the original foil (also called wool foil) made of copper plate after repeated rolling, and roughened according to the requirements. Due to the limitation of calendering process, its width is difficult to meet the requirements of rigid copper clad laminate, so it is rarely used on rigid copper clad laminate;
(2) Electrolytic copper foil is to make copper foil by dissolving copper into solution, then electrodeposition copper sulfate electrolyte under the action of direct current in special electrolytic equipment, and then carry out a series of surface treatment such as surface treatment, heat-resistant layer treatment and anti-oxidation to the original foil according to the requirements.
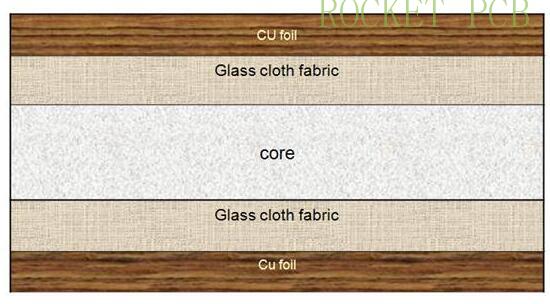
Composite copper clad laminate (CCL) is a kind of rigid copper clad laminate (CCL) which is composed of different reinforced materials. This kind of board is mainly CEM series copper clad laminate. CEM-1 (epoxy paper based core material) and CEM-3 (epoxy glass non-woven fabric core material) are two important varieties in CEM.
It has excellent machinability and is suitable for punching process;
Due to the limitation of reinforced materials, the thinnest thickness is 0. 6 mm and the maximum thickness is 2. 0 mm;
Different fillers can make the substrate have different functions, such as white board and blackboard suitable for LED, high CTI board for household appliance industry, etc;
CEM-1
The structure of CEM-1 copper clad laminate is composed of two different substrates, namely, the fabric is glass fiber cloth, the core material is paper or cellophane, and the resin is epoxy resin. The products are mainly single-sided copper clad laminate;
The characteristics of CEM-1 CCL are as follows: the main performance of CEM-1 is better than that of paper-based CCL; it has excellent machinability; its cost is lower than that of GFRP;
CEM-3
CEM-3 is a composite copper clad laminate with performance level and price between CEM-1 and FR-4. The board is made of glass fiber cloth impregnated with epoxy resin as the surface, epoxy resin glass fiber paper as the core material, and covered with copper foil on one or both sides by hot pressing
CEM reinforced material for composite substrate
Cellophane or cellophane
CEM-3 cellophane
CEM-1 fiber paper
Glass cloth
7628 As the main
Filler
Aluminum hydroxide, talc powder, etc
Composite substrate structure
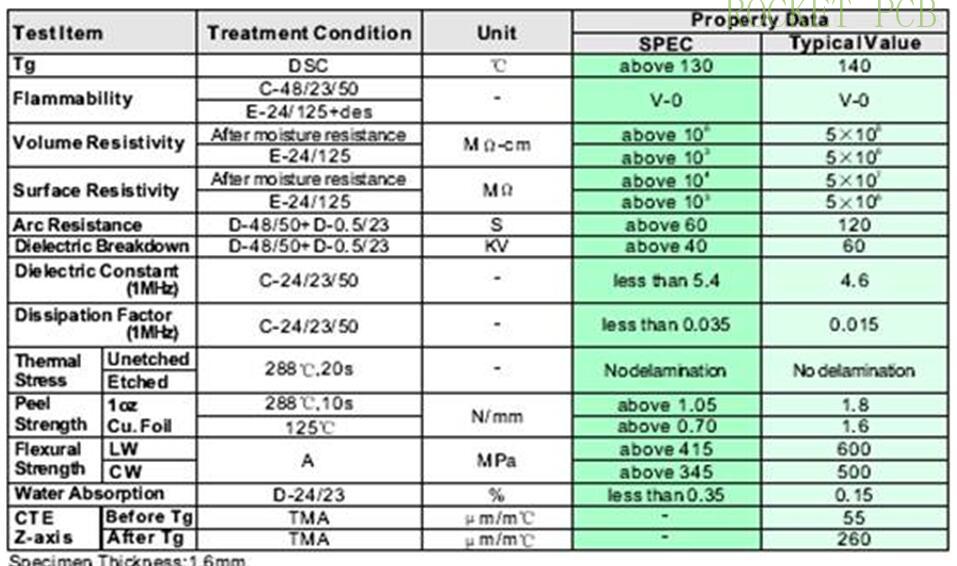
Performance index of Shengyi common FR-4 (S1141)
Sequence lamination circuit board material (HDI) copper clad resin RCC
Copper clad resin RCC
Definition: RCC is formed by coating one or two layers of special epoxy resin or other high-performance resin (the thickness of resin is generally 60-80um) on the coarsening surface of extremely thin electrolytic copper foil (the thickness of resin is generally 60-80um), and the solvent is removed after drying in the oven, and the resin semi-solid sheet reaches the B-level. In the manufacturing process of HDI multilayer board, RCC replaces the role of traditional bonding sheet and copper foil, as the conductive layer of insulating medium, non mechanical drilling technology (usually laser drilling and other new technologies) can be used to form micropores to achieve electrical connectivity, so as to achieve high density of printed circuit board.

Composition of RCC
RCC is composed of coating a layer of high-performance resin composition which can meet the specific performance requirements on the coarsening surface of ultra-thin copper foil, and then drying and semi curing in the oven to form a layer of resin with uniform thickness on the coarsening surface of copper foil. The structure diagram is as follows:

TG temperature
Glass transition temperature (TG)
At present, the TG value of FR-4 board is generally 130-140 degrees. However, in the process of PCB fabrication, there are several problems beyond this range, which will have a certain impact on the processing effect and final state of the products. Therefore, increasing TG is a main method to improve the heat resistance of FR-4. One of the important means is to increase the correlation density of curing system or increase the content of aromatic groups in the resin formula. In general FR-4 resin formula, the TG value is increased to about 160-200 degrees by introducing some epoxy resins with three functional groups and multi-functional groups or by introducing some phenolic epoxy resins
Dielectric constant DK
Dielectric constant
With the rapid development of electronic technology, the speed of information processing and information transmission is increasing. In order to expand the communication channel and transfer the frequency to high frequency field, it requires the substrate material to have low dielectric constant E and low dielectric loss tangent TG. Only by reducing e can we get high signal propagation speed, and only by reducing TG can we reduce signal propagation loss.
Coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE)
With the development of PCB precision, multilayer, BGA, CSP and other technologies, higher requirements are put forward for the dimensional stability of CCL. Although the dimensional stability of CCL is related to the production process, it mainly depends on the three raw materials: resin, reinforcement material and copper foil. The common methods are as follows: (1) modifying the resin, such as modifying epoxy resin; (2) reducing the content of resin, but this will reduce the electrical insulation and chemical properties of the substrate; copper foil has little effect on the dimensional stability of the copper clad laminate
UV barrier property
This year, in the process of circuit board production, with the popularization and use of photosensitive solder paste, in order to avoid the mutual influence of two sides, it is required that all substrates must have the function of shielding UV.
There are many ways to block the transmission of ultraviolet light. One or two of glass fiber cloth and epoxy resin can be modified, such as using epoxy resin with uv-block and automatic optical detection function.
Several high performance material
CAF resistant material
Halogen free board
ROHS standard and RoHS compliant material
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
Copper clad laminate of PPE glass fiber cloth
BT
CAF resistant material
With the rapid development of electronic industry, electronic products are light, thin, short and miniaturized. The hole spacing and line spacing of PCB will become smaller and smaller, and the circuit will be more and more detailed. As a result, the ion migration resistance of PCB becomes more and more important. Ionic migration (CAF) was first discovered by the researchers of Bell laboratory in 1955. It refers to the electromigration chemical reaction of metal ions in non-metallic media under the action of electric field, thus forming a conductive channel between the anode and cathode of the circuit, resulting in the short circuit of the circuit.
Harm of ion migration to electronic products
1)The signal of electronic products becomes worse, and the performance and reliability of electronic products decrease.
2)The service life of electronic products is shortened.
3)Energy consumption increased.
4)Insulation damage may lead to short circuit and fire safety problems.
Four cases of ion migration

Lead, polybrominated biphenyl (PBB) and polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE) are directly related to printed circuit boards. Lead is used for solderable tin lead coating on the connection plate of printed circuit board, which is formed by hot air leveling tin lead solder or electroplating tin lead; PBB and PBDE bromide are used as flame retardant for copper clad laminate and semi cured sheet of printed circuit board substrate, mixed in resin.
High performance PCB material: halogen free material
Definition of halogen free material:
① The flame retardancy reaches UL94 V-0.
② It does not contain halogen (JPCA standard: CL ≤ 900ppm, Br ≤ 900ppm), antimony, red phosphorus, etc. , and has less smoke and odor when burning.
③ In the process of production, processing, application, fire and waste disposal (recycling, burying, burning), no harmful substances will be produced.
④ The general properties are the same as that of common plate and reach ipc-4101 standard.
⑤ The processability of PCB is basically the same as that of common board.
⑥ In the future, it also requires energy saving and recycling.
How to make halogen free PCB
For example, sodium hypophosphite or borohydride is used for electroless copper plating without harmful formaldehyde; hydroxyl sulfonic acid is used to replace fluoroboric acid; tin plating layer is used to replace lead-zinc alloy coating; fluorine-free and lead-free tin plating is used; silver slurry through-hole process is used; and sodium hypophosphite or borohydride is used as reducing agent for electroless copper plating without harmful formaldehyde; hydroxyl sulfonic acid is used to replace fluoroboric acid; tin plating layer is used to replace lead-zinc alloy coatingLead free welding process and so on.
Lead free
(2) There are tin silver solder, tin silver lead solder, tin zinc solder, tin bismuth solder, tin silver bismuth solder and so on. At present, tin silver copper solder (95. 5sn/4ag/0. 5cu) is widely used, and its melting point is 217 ℃. The melting point of this kind of lead-free solder is 34 ℃ higher than that of tin lead solder (63Sn / 37Pb) 183 ℃. Undoubtedly, the temperature should be improved and the temperature resistance of PCB should be improved. The welding temperature of lead-free solder is 30 ℃ - 40 ℃ higher than that of tin lead solder, which requires high glass transition temperature (TG) of PCB substrate and good heat resistance; multilayer board lamination and metallization hole are required to be reliable, without thermal stratification or hole wall fracture. This is the new requirement of lead-free PCB
ROHS standard definition
RoHS is the abbreviation of the restriction of the use of certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment. This directive mainly limits the contents of lead, mercury, cadmium, hexavalent chromium, polybrominated biphenyl (PBB) and polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE) in products.
Hazardous substances not conforming to ROHS standard
RoHS listed six harmful substances, including Pb, cadmium/Cd, mercury/Hg, Cr6 +, PBB, PBDE.
Implementation time of ROHS standard
The European Union will implement RoHS on July 1, 2006. At that time, electrical and electronic products that do not meet the standards will not be allowed to enter the EU market.
RoHS process implementation
At present, the lead-free surface treatment methods used for printed circuit board include coating solderable organic protective layer (OSP), electroless nickel / gold plating, electroless nickel plating, electroless tin plating, electroless silver plating, hot air leveling lead-free solder, etc. Some of these surface treatment methods have been widely used in PCB products, and some are still in promotion. The hot air leveling technology and equipment for lead-free solder have also been put into trial use.
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE): the main substrate of high frequency printed circuit board
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) has symmetrical structure and has superior physical, chemical and electrical properties. Among all resins, PTFE has the smallest dielectric constant and dielectric loss tangent.