The most complete classification of PCB types
PCBs are classified in many ways.
According to the softness of the substrate material, can be divided into rigid board (R-PCB), flexible version (FPC, Flexible Printed Circuit), rigid-flexible combination board.
According to the number of layers of conductive graphics, can be divided into single-sided, double-sided, multilayer board; which, multilayer board can be divided into low and medium layer board and high layer board.
According to the application area, it can be divided into communication boards, consumer electronics boards, computer boards, automotive electronics boards, etc..
In addition, there are special product categories, such as high-speed high-frequency board, high-density connection board (HDI, High-Density Interconnector), packaging substrate.
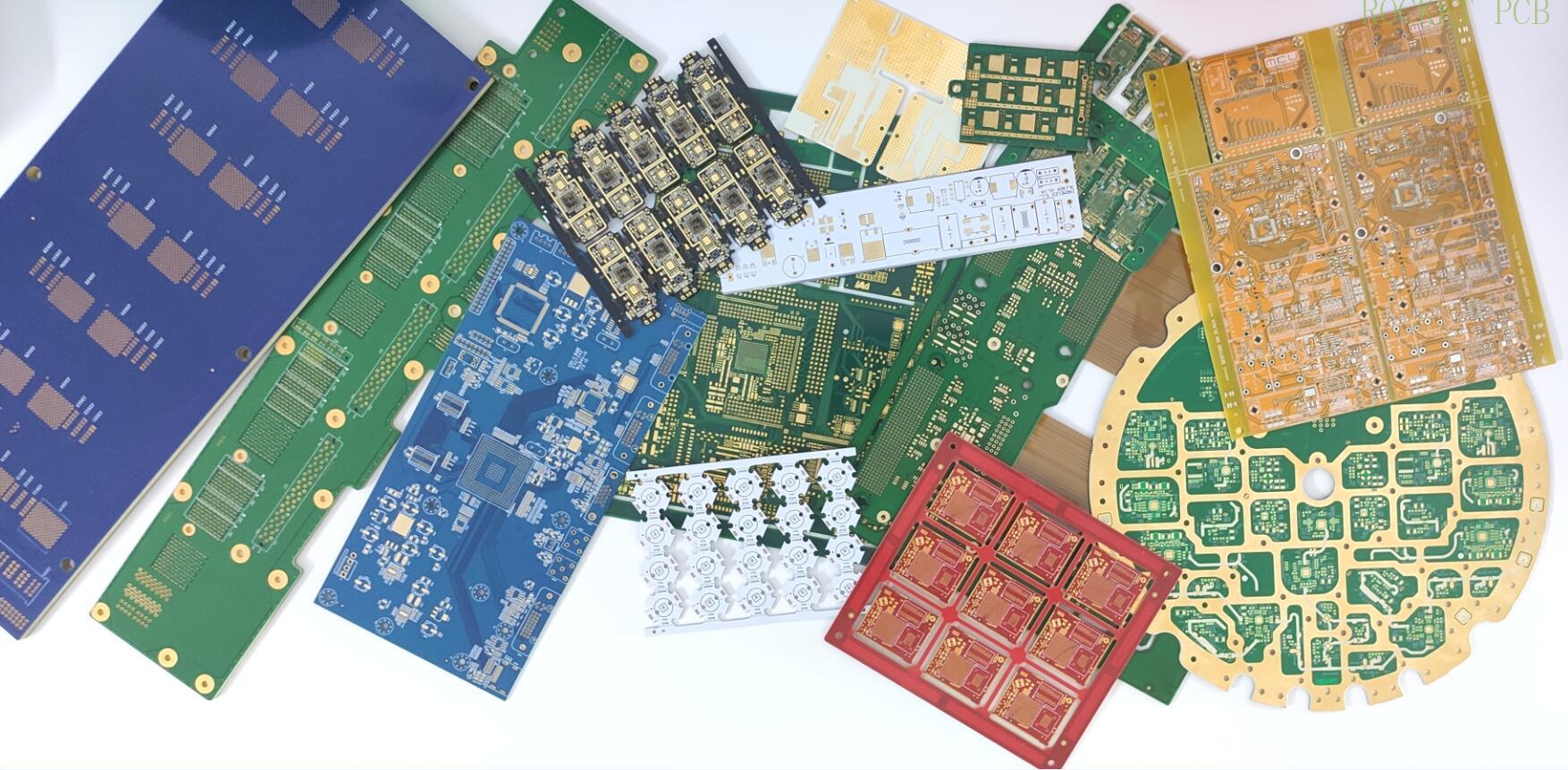
Different types of PCBs, have different characteristics and uses, summarized below
| Product category | Product features | Application area | Chinese mainland manufacturers | ||||
| Rigid board | Single board | The single board only forms the conductive pattern on one side of the insulating substrate, while the wires are concentrated on the other side, which is the most basic structure in the printed circuit board | Ordinary household appliances, electronic remote control, and simple electronic products | There are more mainland PCB manufacturers with the ability to produce single/double-sided boards and ordinary medium and low layer boards | |||
| Double sided board | The double board is a circuit board with an upper and lower circuit structure. Compared with a single board, the application of a double-sided board is basically the same as that of a single board. The main feature is that it increases the wiring density per unit area, and its structure is more complex than that of a single board | Consumer electronics, computer, automotive electronics, communications equipment, industrial control and other fields | |||||
| Multilayer board | Common multilayer board | Medium-low laminate | Medium and low layer boards generally refer to printed circuit boards with 4-6 layers of conductive patterns | Consumer electronics, personal computers, laptops, automotive electronics and other fields | |||
| High rise layer | High-level board refers to the printed circuit board with 8 or more conductive patterns | Communication equipment, high-speed server, industrial control medical, military and other fields | Kinwong electronics, Suntak technology, etc | ||||
| Backplane | Backplane refers to the printed circuit board used to connect or plug multiple single boards in the electronic system to form an independent system. It has the characteristics of high multi-layer, super large size, super high thickness, super weight, high reliability, etc., and the processing technology is difficult, especially in the lamination, drilling, key and other process links (mainly in 20-60 layers, 4-12mm thickness, 30000-100000 holes) | Communication core routing switching, OTN transmission, communication base station, data center service/storage, supercomputer, large medical imaging equipment, and aerospace control system | Fastprint technology, Suntak technology, Founder Technology, etc | ||||
| Metal substrate | Copper substrate | The most widely used and high-end metal-based products have good heat dissipation, good dimensional stability, high cost and high quality | Wireless communication base station, microwave communication and other fields to solve the problem of high-power system heat dissipation | Kinwong electronics, Suntak technology, Fastprint technology, Sunshine circuit, Bomin electronics, CEE electronics, Tianjin Printronics, Xiehe electronics, etc | |||
| Aluminum substrate | Although the heat dissipation performance is not as good as copper substrate, it is relatively light due to its low cost. It has excellent electrical insulation performance and machining performance | It is used in the circuit which produces more heat, such as car igniter, power controller, etc | |||||
| Iron baseboard | It has magnetic function and good magnetic conductivity, but it is easy to oxidize and has high quality | Small precision motor and intelligent driver, etc | |||||
| Stainless steel substrate | It has good acid resistance, weather resistance, high strength, but high quality | It is often used in marine lighting circuit and other harsh environment | |||||
| High speed board | It is made of a multi-layer conductive pattern and low dielectric consumption high-speed material. It mainly undertakes the high-speed circuit signal transmission between chipsets, so as to realize the chip operation and signal processing functions | Communication and service/storage, etc | Fastprint technology, Bomin electronics, etc | ||||
| High frequency board | Also known as RF circuit board, high-frequency circuit board refers to the special circuit board with high electromagnetic frequency, which generally uses ceramics, PPO resin or fluorine resin as the substrate material of circuit board | It can be divided into two categories: 1) high-frequency signal transmission (related to radio electromagnetic wave) electronic products, such as modern communication equipment, satellite radar, radio and television, etc.; 2) high-speed logic signal transmission (digital signal transmission) electronic products.It is mainly used in automobile anti-collision system and automobile braking system | Suntak technology, Bomin electronics, Mingyang circuit, Dongshan precision, Xiehe electronics, etc | ||||
| HDI | Introduction | First order (1 + C + 1), second order (2 + C + 2), third order (3 + C + 3) | Mobile phones, digital cameras and other consumer electronics, communication equipment and automotive electronics and other fields | Fastprint technology, Suntak technology, Olympic circuit, etc | |||
| General category | Fourth-order and above, any layer (n + C + N, currently mostly 10-12 layers) | CEE Electronics | |||||
| High end | SLP, rigid-flex composite board, rigid board area using HDI Technology | Avary Holdings | |||||
| Flexible board | A flexible board, also known as a flexible board, is a printed circuit board made of polyimide or polyester film and other flexible insulating substrates. The flexible board can be bent, wound, folded, arranged according to the space layout requirements, and moved and expanded in three-dimensional space, so as to achieve the integration of component assembly and wire connection | Smartphones, tablets. Wearable devices, other touch devices, etc | More mainland manufacturers have the ability to produce flexible boards | ||||
| Rigid-Flex PCB | Also known as "soft and hard combination board", it refers to laminating different flexible boards and rigid boards together, realizing the coarse interconnection of the rigid printed circuit board and flexible printed circuit board through-hole metallization process, the flexible board can be bent and rigid board can bear heavy components, forming a three-dimensional circuit board | Medical equipment, navigation system, consumer electronics, etc | |||||
| Packaging substrate | Memory chip package substrate (EMMC) | Smartphone memory module, solid-state hard disk, etc | Shennan circuit (SCC), danbang technology, Fastprint technology | ||||
| MEMS packaging substrate | Smartphones, tablets, wearable devices, sensors, etc | ||||||
| RF module packaging substrate RF | RF module of mobile communication products such as smartphones | ||||||
| Processor chip package substrate (WB-CSP and FC-CSP) | Baseband and application processor of smartphones, tablet computers, etc | ||||||
| High speed communication package substrate | Data broadband, telecommunication, FTTX, data center, security monitoring, and smart grid conversion module | ||||||