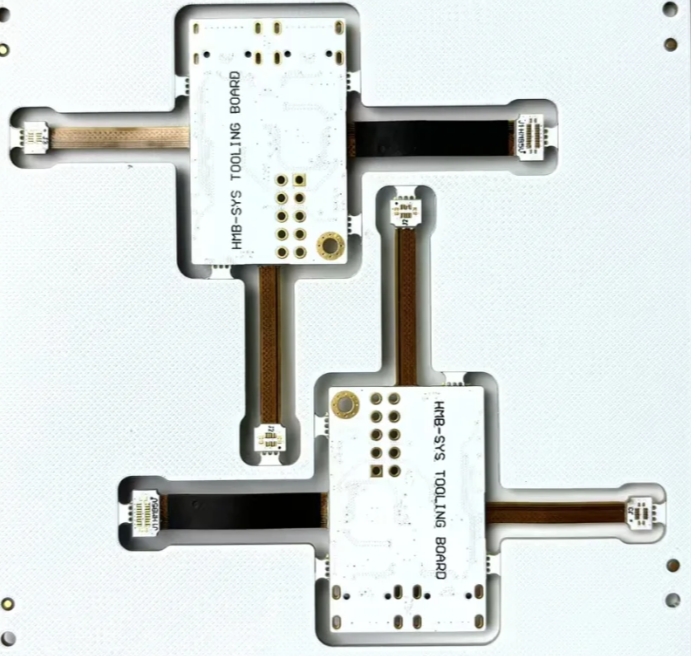
What is the difference between rigid flex and semi-flex pcb?
Printed circuit boards are the foundation of modern electronic products. In daily life, there are PCBs hidden in all the electrical products we can see. The most common type of PCB is rigid PCB, but rigid PCB has no flexibility, does not allow bending or stretching, and has no way to be applied in complex 3D circuit layouts with limited space. So flexible PCB (also called flexible PCB) was born, which uses thin and bendable materials such as polyimide. However, pure rigid and pure flexible PCB represent two extreme cases. Rigid PCB provides reliability but no flexibility, while flexible PCB provides unlimited bending but lacks structural rigidity. And with the rapid development of modern electronic products, many electronic products require to be thinner, more compact and more beautiful in order to win the favor of customers. However, while requiring to reduce the spatial layout, the integration and complexity of internal electronic components continue to increase. This requires our PCB industry to continuously develop new products.
1. Technical features of Semi-Rigid Flex PCB
In terms of structure and materials: Semi-rigid flexible boards are usually based on flexible substrates, with rigid support materials (such as FR-4) added only in specific areas to enhance local strength and stability. The rigid part is usually small and is mainly used to support key components or connection points, while the flexible part occupies the main area and is suitable for applications that require frequent bending or folding. In terms of design, it pays more attention to local rigid support, which is suitable for applications that require local enhancement but are still mainly flexible overall. The bending radius and angle design are relatively simple, and are usually used for medium-complexity space layouts.
2. Technical features of Rigid-Flex PCB
Rigid-Flex PCB is made of rigid substrate and flexible substrate combined by lamination process. The rigid part and the flexible part are closely combined in the design to form a whole. The rigid part is usually used to install electronic components, while the flexible part is used to connect different modules to adapt to complex spatial layout. Rigid-Flex PCB is more complex than Semi-Rigid Flex PCB in design. It supports multi-bending, multi-stackup and multi-zone characteristics, and can realize three-dimensional spatial layout. The bending radius and angle design are more flexible, suitable for highly complex space requirements, such as foldable devices or high-density integrated electronic products. For example, small and high-density integrated electronic products such as mobile phones.
3. Materials and manufacturing process
Rigid-Flex PCB: It is formed by lamination using FR4 (rigid part) and polyimide (PI, flexible part). The manufacturing process is complex, involving lamination of rigid boards and flexible boards, multi-stackup design, etc., and the cost is relatively high. Dynamic bending can be performed in the flexible area, which is suitable for applications that require frequent folding or bending, such as flip phones or medical devices. Suitable for applications with high reliability requirements.
Semi-Rigid Flex PCB: Mainly based on polyimide (PI) flexible substrate, some areas are reinforced by FR4 or other reinforcing materials, but no complete rigid PCB layer is used. It can only be bent once during the manufacturing process, and then a fixed shape is formed. It cannot be bent repeatedly, otherwise it may cause breakage. The manufacturing process is relatively simple and the cost is low, which is suitable for small and medium batch production. Due to the small number of rigid parts, the material and process requirements are relatively low.
4. Application scenarios
Rigid-Flex PCB: Suitable for applications that require local rigid support but are still mainly flexible as a whole, such as some wearable devices, sensor modules or small electronic devices, and are cost-sensitive and do not require highly complex designs.
Application examples: smart phones, camera modules, medical electronics, aerospace products, automotive electronics, etc. .
Reliability: High reliability, suitable for applications with high stress and frequent bending. By reducing connectors and solder joints, the stability and durability of the connection are significantly improved.
Semi-Rigid Flex PCB:
Suitable for applications that require local rigid support but are still mainly flexible, and circuits that require a specific shape but will not bend again, such as communication equipment, sensor modules or small electronic devices.
Application examples: servers, wearable devices, sensor modules.
Reliability: Medium reliability, suitable for applications with medium stress and bending times. Due to the small number of rigid parts, local stress concentration problems may occur during long-term use.
Comparison summary
Feature | Semi-Rigid Flex PCB | Rigid-Flex PCB |
Structure | Primarily flexible substrate with localized rigid support materials | Rigid and flexible substrates tightly integrated into a single unit |
Design Complexity | Moderate, suitable for applications requiring localized rigid support | High, supports multi-bending, multi-stackup, and multi-zone designs |
Bending Capability | Can only be bent once during manufacturing to form a fixed shape | Supports dynamic bending, suitable for frequent folding or bending applications |
Manufacturing Process | Relatively simple, lower cost | Complex, higher cost |
Application Scenarios | Communication devices, sensor modules, small electronic devices | Smartphones, camera modules, medical electronics, aerospace products, etc. |
Reliability | Moderate, suitable for applications with medium stress and bending cycles | High, suitable for high-stress and frequent bending applications |
If you need a true rigid + flexible combination, and the circuit board part can still bend, choose Rigid-Flex PCB.
If you just want to enhance the rigidity of the flexible board in a certain area, but do not intend to let it bend dynamically, choose Semi-Rigid Flex PCB.
Both have their advantages, and the specific choice depends on the application requirements!